Safflower seeds prevent kidney damage caused by chemotherapy
04/12/2019 / By Ralph Flores
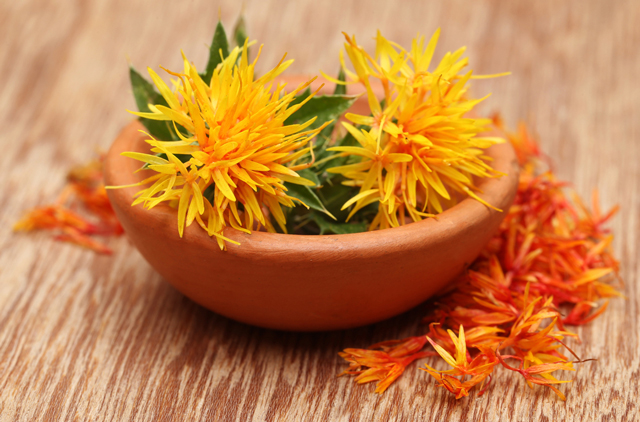

Safflower seed extracts can protect the kidneys from the adverse effects brought about by cisplatin treatment, according to a multi-university study in South Korea. Their findings appeared in The American Journal of Chinese Medicine.
- The researchers investigated whether extracts from safflower seeds can have pleiotropic effects in vivo.
- For the study, mice were intraperitoneally injected with cisplatin at 20 milligrams per kilogram (mg/kg) of body weight to induce renal failure.
- Mice in the experimental group were treated with either a 100 or 200 mg/kg oral safflower seed extract two days before cisplatin was administered.
- Researchers took serum and renal biochemical factors three days after cisplatin injection. These included oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis-related protein expression. In addition, they took samples for histological analysis.
- Mice in the control group exhibited losses in body weight and food and water intake, as well as increased kidney weight. However, those pre-treated with safflower seed extracts did not show similar symptoms.
- Safflower seed extract also reduced the levels of reactive oxygen species in the kidney after cisplatin treatment, as well as decreased serum urea nitrogen and creatinine levels.
- While protein expression related to antioxidant defenses was downregulated after cisplatin, safflower seed extract upregulated the expression of catalase. It also modulated the expression of phosphor (p)-p38, nuclear factor-kappa B p65, cyclooxygenase-2, inducible nitric oxide synthase, ATR, p-p53, Bax, and caspase 3 proteins.
- Histological analysis revealed that mice treated with safflower seed extract did not have significant renal damage.
In sum, safflower seed extracts attenuated both oxidative stress- and apoptosis-related markers and exhibited renoprotective activity in mice treated with cisplatin.
Journal Reference:
Park CH, Lee AY, Kim JH, Seong SH, Jang GY, Cho EJ, Choi JS, Kwon J, Kim YO, Lee SW, et al. PROTECTIVE EFFECT OF SAFFLOWER SEED ON CISPLATIN-INDUCED RENAL DAMAGE IN MICE VIA OXIDATIVE STRESS AND APOPTOSIS-MEDIATED PATHWAYS. The American Journal of Chinese Medicine. 3 January 2018;46(01):157–174. DOI: 10.1142/S0192415X1850009X
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
alternative medicine, cisplatin, disease treatments, herbal medicine, Herbs, kidney damage, kidney health, natural cures, natural medicine, prevention, remedies, renal damage
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author