Man Jing Zi, a powerful TCM, found to hold great anticancer potential
06/13/2019 / By Evangelyn Rodriguez

The plant Vitex rotundifolia, known as beach vitex in English and man jing zi in traditional Chinese medicine, is widely studied for its medicinal properties. The ancient Chinese used it to treat a wide variety of ailments, ranging from eye problems and headaches to menstrual disorders. But what beach vitex is well-known for today is its anticancer activity. Several studies show that beach vitex can be a potent antiproliferative agent against various cancer cells, including breast, lung, and colorectal cancer. A recent study conducted by researchers from Andong National University in South Korea investigated the mechanisms behind its biological activity against colorectal cancer cells, particularly its inhibitory effect on the down-regulation of cyclin D1 and CDK4, which are proteins associated with cancer cell proliferation. The results of their study were published in The American Journal of Chinese Medicine.
Beach vitex and its health benefits
Beach vitex is a salt-tolerant shrub known for its therapeutic properties. In TCM, beach vitex, particularly its leaves and fruit (Victis Fructus, VF), are used to treat inflammation, headache, migraine, chronic bronchitis, eye pain, and gastrointestinal infections. Recognized by its Chinese name man jing zi, VF is believed to act on the Bladder, Liver, and Stomach channels to disperse wind and clear heat. It is also used in combination with other herbs to make herbal remedies for maladies that involve swelling, spasms, and pain.
The herbal medicine man jing zi is also used to treat menstrual and menopausal disorders. Man jing zi is said to increase the production of luteinizing hormone, a hormone that controls the ovarian function in females and testes function in males. It also inhibits the release of follicle-stimulating hormone, which shifts the ratio of estrogens to gestagens in favor of the latter and causes a corpus luteum hormone effect. Man jing zi helps normalize milk production, regulates menstruation, stimulates progesterone synthesis, and regulates estrogen to alleviate symptoms of PMS and menopause.

Studies done on beach vitex have resulted in the discovery of many of its chemical components. VF and the leaves of beach vitex contain a variety of phytochemicals, such as flavones, monoterpenes, diterpenes, alkaloids, sesquiterpenoids, glucosides, and aryl napthalenes norlignans. Other components of beach vitex that have notable biological activities according to in vitro studies are as follows:
- Casticin – A flavonoid that inhibits human cancer cell growth.
- Polymethoxyflavonoids – Compounds that limit proliferation of human myeloid leukemia cells by inducing apoptosis.
- Ferruginol – A diterpene that exhibits antioxidant activity.
- Vitexicarpin – A flavonoid that inhibits t-lymphocyte proliferation and the growth of two cancer cell lines; also exhibits anti-inflammatory effects against immune-regulatory disorders.
- (+)-polyalthic acid – A compound found in VF that exhibits antimutagenic activity.
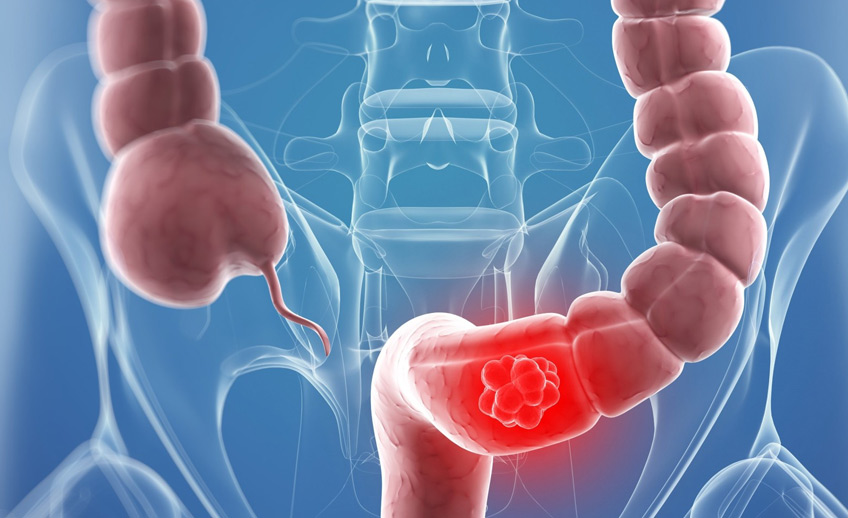
Dried fruits of beach vitex show antiproliferative activity against human colorectal cancer cell lines
Korean researchers recently investigated the inhibitory effect of VF on the down-regulation of cyclin D1 and CDK4, two proteins associated with cancer cell proliferation. The molecular mechanisms by which VF inhibits the proliferation of cancer cells have not been elucidated in detail. Based on their experiments, the researchers reported the following:
- VF suppressed the proliferation of human colorectal cancer cell lines HCT116 and SW480.
- VF decreased cyclin D1 and CDK4 in both protein and mRNA levels.
- VF decreased the protein levels of cyclin D1 and CDK4 via proteasomal degradation.
- In cyclin D1 and CDK4 degradation, Thr286 phosphorylation of cyclin D1 plays a pivotal role in VF-mediated cyclin D1 degradation.
- Experiments with several kinase inhibitors suggest that VF-mediated degradation of cyclin D1 may be dependent on GSK3B.
- VF-mediated degradation of CDK4 is dependent on ERK1/2, p38, and GSK3B, which are all mediators of cell apoptosis.
- In the transcriptional regulation of cyclin D1 and CDK4, VF inhibited Wnt activation associated with cyclin D1 transcriptional regulation through TCF4 down-regulation.
- VF treatment down-regulated c-myc expression-associated CDK4 transcriptional regulation.
The results demonstrated that the anticancer activity of beach vitex fruit or man jing Zi is due to its ability to suppress the expression of proteins necessary for cell proliferation. The researchers concluded that VF has the potential to be a candidate for the development of chemoprevention or therapeutic agents for human colorectal cancer.
Sources include:
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
alternative medicine, anticancer, Beach vitex, cancer cures, chemoprevention, Colorectal Cancer, disease treatments, dried fruit, herbal medicine, Herbs, natural cures, natural medicine, phytochemicals, prevention, remedies, research, TCM, therapeutic agents, traditional Chinese medicine, Victis Fructus, Vitex rotundifolia
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author