Tannin from Sanguisorba officinalis exhibit potential anti-cancer properties
02/13/2020 / By Evangelyn Rodriguez
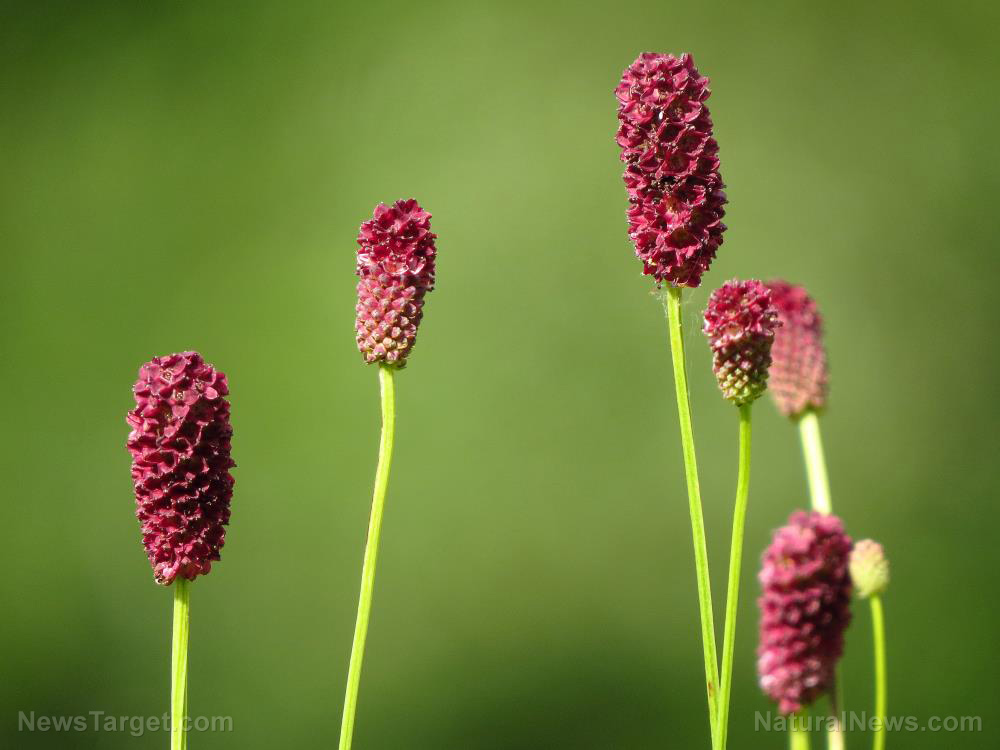

In this study, researchers from China identified the active compound and molecular mechanism of Sanguisorba officinalis against the Wnt/B-catenin signaling pathway, and developed Wnt inhibitors from natural products as anti-colorectal cancer agents. Their results were published in the journal Chinese Medicine.
- S. officinalis or di yu is a popular Chinese herb that can inhibit the growth of many human cancer cell lines, including colorectal cancer cells.
- Using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), the researchers obtained 1,4,6-Tri-O-galloyl-B-D-glucopyranose (TGG) from S. officinalis.
- They performed MTT assay to determine the effect of TGG on the proliferation of NIH3T3 (mouse embryonic fibroblasts) and HT29 (human colon adenocarcinoma) cells.
- To investigate the activity of Wnt/B-catenin signaling in NIH3T3, they used luciferase reporter assay. mRNA and protein expression levels were detected by RT-PCR and Western blot.
- The researchers also performed immunofluorescence assay to measure the levels of B-catenin in the cytoplasm and nucleus.
- Lastly, they conducted transcriptomic profiling study to investigate the molecular mechanism behind TGG’s effect on the Wnt/B-catenin signaling pathway.
- The researchers found that TGG significantly inhibited the Wnt/B-catenin signaling pathway and down-regulated the expression of B-catenin and Wnt target genes (Dkk1, c-Myc, FGF20, NKD1, Survivin).
- TGG also up-regulated the levels of cleaved caspase3 and cleaved PARP, as well as the ratio of Bax/Bcl-2, which may explain the apoptosis of HT29 cells.
Based on these findings, the researchers concluded that TGG from S. officinalis can inhibit Wnt activity and has the potential to become an anti-colorectal cancer agent.
Read the full article at this link.
Journal Reference:
Li W, Yang CJ, Wang LQ, Wu J, Dai C, Yuan YM, Li GQ, Yao MC. A TANNIN COMPOUND FROM SANGUISORBA OFFICINALIS BLOCKS WNT/?-CATENIN SIGNALING PATHWAY AND INDUCES APOPTOSIS OF COLORECTAL CANCER CELLS. Chinese Medicine. 31 May 2019;14(1). DOI: 10.1186/s13020-019-0244-y
Tagged Under: alternative medicine, anticancer, cancer cures, Chinese medicine, great burnet, herbal medicine, Herbs, natural cures, natural medicine, plant medicine, remedies, research, TCM