The in vitro anti-cancer activities of Ocimum sanctum leaf extracts (holy basil)
06/29/2020 / By Evangelyn Rodriguez
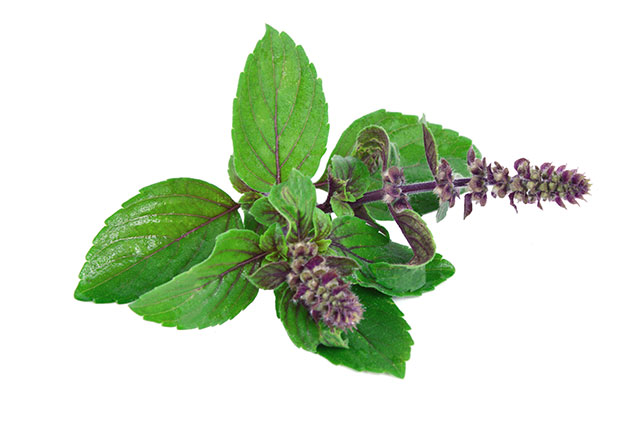

In this study, a researcher at Government Degree College, Khairatabad in India investigated the anti-cancer activity of plant suspension cultures of Ocimum sanctum (holy basil) against lung cancer. Key findings were published in the International Journal of Green Pharmacy.
- Ethanol, acetone and aqueous leaf extracts of O. sanctum were used to treat human lung cancer (A549) cells. Their in vitro anti-cancer activity was evaluated using MTT assay and trypan blue dye exclusion assay.
- The former is based on the capacity of mitochondrial enzymes of viable cells to reduce MTT, a yellow soluble salt, to purple-blue insoluble formazan precipitate. This is quantified using a spectrophotometer at 570 nm.
- The latter, meanwhile, is based on cell staining and is used to quantify the number of viable cells present in a cell suspension.
- Cells are then counted using a hemocytometer under a microscope, where non-viable cells will be stained blue and viable cells will remain unstained.
- The researchers reported that the aqueous leaf extract of O. sanctum did not show anti-cancer activity, but its acetone and ethanol leaf extracts did.
- The acetone leaf extracts displayed the highest anti-cancer activity against human cancer cells at a concentration of 40 to 50 mcg/mL.
Based on these findings, the researchers concluded that O. sanctum acetone and ethanol leaf extracts have anti-cancer properties and can be used against lung cancer.
Journal Reference:
Yadavalli V. EVALUATION OF ANTICANCER COMPOUNDS FROM SUSPENSION CULTURES OF HOLY BASIL (OCIMUM SANCTUM L.). International Journal of Green Pharmacy. 2019;13(2):98. DOI: 10.22377/ijgp.v13i2.2487
Tagged Under: alternative medicine, anticancer, cancer cures, cancer treatments, food cures, food is medicine, functional food, herbal medicine, Herbs, holy basil, natural cures, natural medicine, remedies, research